STEP 15
Vocabulary
![]() Read and memorize this nouns and adjectives.
Read and memorize this nouns and adjectives.
Nouns
Dress |
 |
Drink |
 |
Earth |
 |
Field |
 |
Foot |
 |
Parcel |
 |
Reading |
 |
Spade |
 |
Stocking |
 |
Week |
 |
Change |
|
Walk |
|
Adjectives
Opposite
Tired
Structure words
Send
Among
Through
Together
Structure
1. Nouns
The plural of “foot” is irregular.
- Foot – Feet
- Some of the girls are still awake.
- The opposite wall has no pictures.
- The two houses are at opposite sides of the field (that is, one house is at one side and the other at the opposite side).
- The men opposite (to) us have spades.
- The field is opposite the house.
- 3. Operators
- I send parcels to my sister frequently.
- The store sends meat to our house every week.
- They will send a boat with food and drink for the island.
- Someone sent these flowers to my mother.
- You sent no books from the library today.
- I sent my friend a dress for her daughter.
- His mother may send him a parcel.
- His work is making sails.
- Keeping the window open for a short time will let the smoke out.
- What was your reason for saying that?
- This is the drain for taking water from the field.
- Getting no answer made the man angry.
- She will come back after sending the parcel.
- My sister kept the stockings for a week before giving them to me.
- His coming as not the reasons for her going.
- Reading a book gives me pleasure.
- Let us take the earth off the potatoes.
- Let us say nothing to him.
- Let us be the first persons there.
- Let us make a change in the advertisement.
- There are fishes among the dark plants under the water.
- Do not put the bad apple among the good ones.
- He got through a hole in the wall.
- There is no other way through the town.
- These curtains let the light through.
- These curtains let the light through.
- Keep your feet together. (Place)
- The girls put their hand up together and said, "I have the answer." (Time)
- The workmen went across the field together.
- We had a meal together.
- Why did he come?
- Put your name on the parcel before you send it.
- We got warm because we did work in the field.
- My mother was tired after the journey to London.
2. Adjectives
“Awake” is not used before a noun.
“Opposite” is an adjective naming a relation between one thing and another. Though it may come before its noun, it is often used like a preposition, or with to after it, coming before the noun or pronoun naming that which the first-named thing is said to be opposite.
Root Form |
Past |
Present |
Future |
SEND |
SENT |
SEND |
WILL SEND |
|
|||
But He, She, It SENDS |
We come now to the Past forms of operators, so learn the Past as well as the Present and Future Forms of send, which is the last of the operators.
It will be seen from the above examples that the object of “send” may be followed by “to” and “an indirect object”. Sometimes “to” is omitted and the indirect object put before the direct object, the same rules applying as in the case of give
The Past Forms of all the operators except “be” are the same for all persons, singular and plural.
You will have noticed that the Past of send is formed by changing the letter at the end. The other operators which form the Past in a similar way, some with a vowel change in addition, are:
DO They did little work at night.
The walk did not make me tired.
Did the fishes get out of the net?
HAVE The church had a loud bell.
We had no drink for the journey.
The girls had a walk1 by the sea.
KEEP I kept his first tooth for a long time.
The women kept their hats and coats on.
MAKE The man made a hole under the roof.
Clouds made the sky dark.
SAY A voice from the opposite side of the room said, "Will you give me an answer to my questions?
The girls said to their mother, "Peter is putting his tongue out."
SEE The dress which I saw in the store is not here today.
In the morning the seamen saw land form their ship.
Another group of operators forms the Past by changing only the middle vowel:
COME No sound came from the direction of the prison.
Some workmen with spades came into the field.
GET She got a parcel this morning.
Some sand got in his eye.
His hands got a grip of the rail.
GIVE He gave the manager his name.
The seaman gave the boat a push.
(Note that in the Past form, in addition to the middle vowel being changed, the final “e” is dropped.)
TAKE She took one of her stockings off and kept the other on.
My friends took me to a beautiful place.
One operator forms the Past by the addition of -ed. 2
SEEM The old man seemed tired at the end of the day.
All the answers seemed clear.
There are two operators whose Past forms bear no resemblance to the Present Form:
BE I was on the opposite side of the street when I saw him.
The drink was bitter.
Was the dress a blue one?
You were putting a cord round the parcel.
Why were we having an argument?
The gloves were almost new, but there were holes in them.
GO A drop of water went on the book.
The boys went to the harbor because a ship was coming in.
Finally, there are two operators which make no change for the past form. The only difference between the Past and the Present is that in the Past no s is added for the Third Person Singular.
LET The store let her take the stockings.
The birds let me come quite near before they went off the branch.
PUT The man put his spade into the earth.
After our walk, we put our tired feet in warm water.

The “-ing” forms of the operators, which have already been used as adjectives, may also be used as nouns naming the activity. As nouns, they may still be followed by an object, adverb, etc. They come under the same rules as names of substances except that they are never used with “a” or in the plural and are very seldom preceded by descriptive adjectives.
Note the use of a possessive adjective before the -ing noun to indicate the doer.
“Reading” is a noun of the same sort:
An order or request is, as you already know, expressed by using the root form of the operator without a subject. A request for action in which the speaker himself intends to take part is made by using “let us” in this way.
4. Prepositions
Two further prepositions are introduced in this Step, “among” and “through”.
AMONG is used only when more than two things are being referred to. We say between when the number is restricted to two.
Through is also used adverbially.
“Though” is also used adverbially.
5. Adverbs
The adverb “together” is used in connection with both place and time.
Exercises
1. Fill in the blanks in the sentences describing these pictures, using Past forms in the case of operators.
 |
A woman _____ into a _____. She _____ on a very long _____. |
|
She _____ the plant in a box and _____ a _____. |
She _____ some flowers _____ the trees. |
She _____ the parcel to her mother who _____ a book in her hands. She _____ "I _____ a _____ this morning and I _____ this.". |
||
She _____ _____ a hole in he wall. |
She _____ a seat because she was _____. |
||
She _____ a plant up with a _____. |
She _____ off her _____ and _____ her _____ in a basin of water. |
||
A woman _____ into a _____. She _____ on a very long _____. |
She _____ the plant in a box and _____ a _____. |
2. Answer in Basic the following questions about the story illustrated in the pictures on above:
(a) Who had a walk?
A:
(b) Where did the woman see the flowers?
A:
(c) How did she get out of the field?
A:
(d) How did she get the plant out of the earth?
A:
(e) What did she put back in the hole?
A:
(f) Where did she put the plant?
A:
(g) What did she give to her mother?
A:
(h) What was her mother doing?
A:
(i) What did she do before she put her feet in water?
A:
(j) Who go some warm drink for her?
A:
3. Write sentences about these pictures, bringing in each preposition in a separate sentence. The numbers in brackets under each picture indicate the number of prepositions that it illustrates.
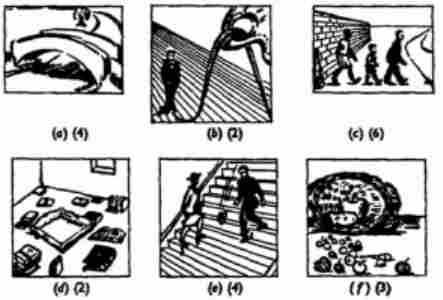
You now know all the prepositions. The six pictures below illustrate all the prepositions that actually name directions or positions, and also the prepositional phrase out of.
1.-
2.-
3.-
4.-
5-
6-
4. Put the following sentences into the Past Tense:
(a) Will they have a walk before they go to the pictures?
A:
(b) They send a parcel to us every week.
A:
(c) Someone lets the bath water out before I am ready.
A:
(d) Some of the flowers in the field are yellow.
A:
(e) These stocking will not get holes in them.
A:
(f) The dress which you have on seems old.
A:
(g) Reading sometimes makes my eyes tired.
A:
(h) The workman takes his spade to the opposite side of the field.
A:
5. Re-write these sentences to introduce an -ing form used as a noun into each of them without changing the sense:
A:
A:
A:
A:





